

Vapor pressure of pure species i at the T of the system Chemical Reaction Engineering Group, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia The liquid phase is an ideal solution→ i 1 → Apply when the species that are chemically similarįor pure species in equilibrium and ideal gas vaporįi fi l fi v P Pisat Vapor-phase mole fraction The vapor phase is ideal gas → ˆi 1 → Apply for low to moderate P 2. VLE (Chapter 11) Consider a multicomponent system in VLE, the fugacity of species i for each phase For vapor mixture T-x1 Similar shape to previous figure (right)

This diagram is of practical interest as most VLE applications occur at const P (e.g. Note: THF, tetrahydrofuran CCl4, carbon tetrachloride CCl3, chloroform Pxy Diagram at Constant T THF(1)/CCl4(2) at 30˚Cġ60 Dashed lines: Px relation for Raoult’s law Portion of a PT diagram in the critical region. P-T Diagram PT diagram for several compositions. Chemical Reaction Engineering Group, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Note: Species 1 has higher vapor pressure or lower boiling point than species 2. Most chemical processes operate at this P, T range Pxy Diagram for 3 T &Txy Diagram for 3 P Saturated vapor (dew line) G: Gas mixture LV: Tie line AEDBLA gives Pxy phase diagram at const. PTxy Diagram for VLE (Cont.) F: Liquid solution L: Bubblepoint W: Dewpoint Under surface is saturatedvapor (P, T, y1 surface) Below that is gas phase Top surface is saturated-liquid (P, T, x1 surface) Above that is liquid phase T curve for species 2Ĭ1 & C2 = critical point for species 1&2 Species 1 is more volatile PTxy diagram for VLE Chemical Reaction Engineering Group, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Binary mixture for species 1 and 2 RKAC1: vapor pressure vs. PTxy Diagram for VLE There are several diagram to describe the behavior for a mixture in the equilibrium phase.
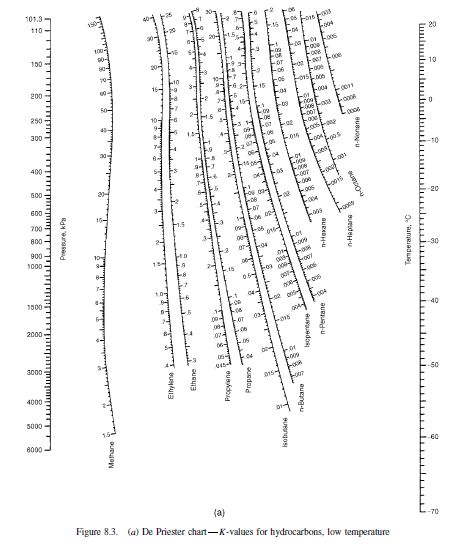
įor any closed system form initially from given masses of prescribed chemical species, the equilibrium state is completely determined when any 2 independent variables are fixed. Molar mass of a mixture or solution: mole-fraction-weighted sum of the molar masses of all species present: Measure of Composition (Cont.) For flow processes convenience suggest its expression as a ratio of Measure of Composition Mass or mole fraction : Mole species i → Fixed temperature, pressure and phase composition In the macroscopic properties of a system with time.Īn isolated system consisting of liquid and vapor phases in intimate contact eventually reaches a final state wherein no tendency exists for change to occur within the system The Nature of Equilibrium Equilibrium: a static condition in which no changes occur Simple Model for VLE K-values Using DePriester Chartĭistillation, absorption, and extraction bring phases of different composition into contact.īoth the extent of change and the rate of transfer depend on the departure of the system from equilibriumįor quantitative treatment of mass transfer the equilibrium T, P and phase compositions must be known. Liquid Phase Properties from VLE data Qualitative Behaviour Carry out flash calculation in order to determine the vapor/liquid fraction as well as the mixture composition of each phase at specified conditions using available K-Values etc.Ĭhemical Reaction Engineering Group, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia. Carry out bubble and Dewpoint calculations for a given mixture. Apply Raoult’s law and Henry’s law to solve simple thermodynamic problems. Apply simplified VLE equations to obtain data for P-XY, T-XY and X-Y diagrams. VLE for high pressure system o VLE from equation of state. Introduction to equilibrium systems The equilibrium criteria and stability The phase rule – Duhem’s theorem Introduction to vapor/liquid Equilibria (VLE) VLE Behaviour and models VLE for low to moderate pressure system o Raoult’s Law -Ideal gas and ideal solution (simple model) o Modified Raoult’s Law o Henry’s Law #Depriester chart ethane 100 kpa how to
Describe the behaviour of VLE and how to simplify the VLE problem. It is expected that students are able to: Mohd Asmadi Bin Mohammed Yussuf Faculty of Chemical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, 81310 UTM Johor, Johor Bahru, Malaysia Chemical Reaction Engineering Group, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia CHAPTER 10 Vapor/Liquid Equilibrium (VLE): Part 1







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
